DHOBI GHAT
2017 - 2018
This project aimed at solving the water system in and around the Dhobi Ghat, and coming up with an incremental green system design that can be implemented in the target location and further can be implemented in all the various locations in Maharashtra.
Green Design

Dhobi Ghat - A place where the traditional DHOBI caste of washermen and women go to wash clothes.
Location: Pune, Maharashtra.
Located in the city of Pune, This specific DHOBI GHAT was built during British rule. Then owned by the washermen community, is still being used by
their descendants.

ELEMENTARY RESEARCH
-
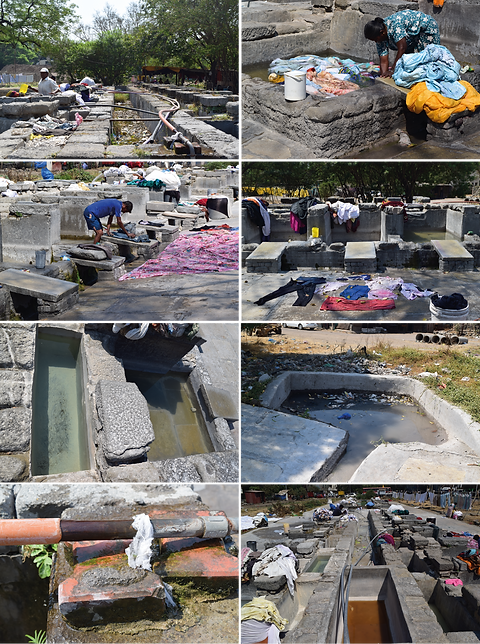
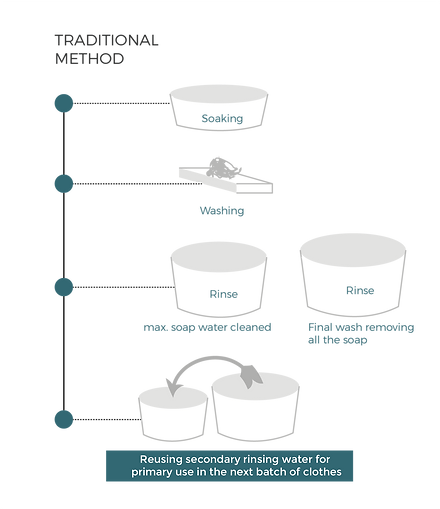
The structure (Cubicle) comprises 3 main compartments :
1. SOAKING
Clothes are soaked in soap water in this compartment.
2. FIRST RINSE
Once the clothes are washed, they are transferred into the 1st rinsing compartment. This stage of the washing removes 70% of the soap from the clothes.
3. SECOND RINSE
Gives a final wash to the clothes removing the leftover soap residue.
-
Structures are placed in a
straight line facing each other.
-
2 cubicles are provided per washerman.
-
Water is filled twice in each of the cubicles every day.
ANALYSIS
Each cubicle holds approximately
1500 liters of water
Each cubicle is filled twice a day
i.e. 3000 liters per cubicle per day
There are 40 cubicles in the area
i.e. 1,20,000 liters per day
There are around 5 such Dhobi Ghats in Pune
i.e. 6,00,000 liters per day
And it keeps growing...

WATER SYSTEM STUDY

OBSERVATIONS
When asked about body pains and posture problems,
‘Being habituated to the style of washing,
the position for washing doesn't affect us.’
WATER
-
There are no taps but only one main water line connected to pipes which can be moved wherever needed.
-
No proper water supply.
-
No water processing before disposal.
-
High level of water consumption.
-
Cubicles filled with water 24*7.
-
No proper drainage system.
DHOBI
-
Work in harsh weather conditions.
-
Highly exposed to the sun.
-
Washing is done standing in the water-filled cubicle.
CHALLENGE
Incorporating various existing simple and cost-effective ideas, bringing improvement in the existing system, and bringing a significant change in the environment.
Inspiration: The traditional washing technique in desert areas
-
Multiple washing steps.
-
ReUse the final wash water for a first wash in the second round.
-
Amount of water used for each step determined by its function.
-
Final greywater used for flushing purposes.
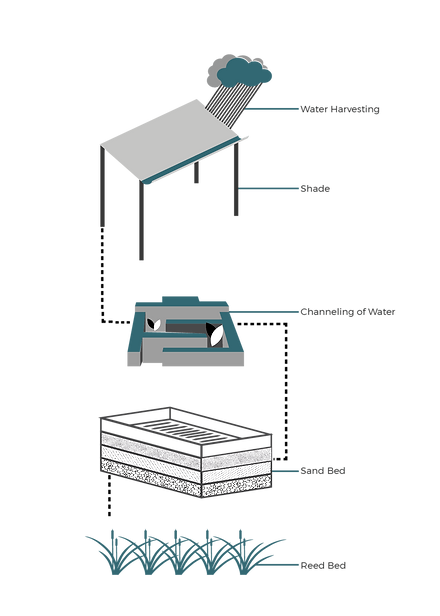
WATER HARVESTING
-
Retaining groundwater and using the same through borewell.
CHANNELING OF WATER
Inspiration: The traditional water channeling method through a maze-like structure.
-
While the water flows through the maze, large particles like leaves, plastics, etc accumulate at the corners leaving only water to flow to the end of the channel.
SAND BED
-
Purifies almost 85% of the water.
-
Chemical-free and no maintenance.
REED BED
-
Reduces ammonia levels as well as BOD and Phosphate levels in the water.
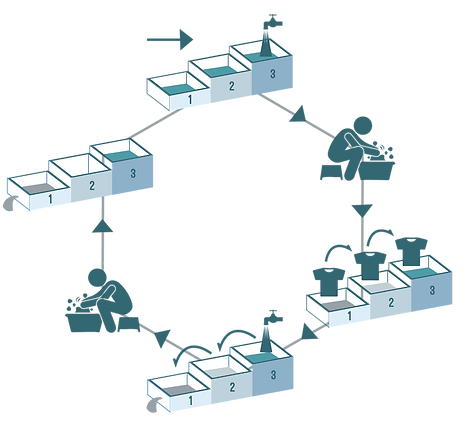
IDEAL WASHING SYSTEM
Fill water in the cubicles
Wash the clothes
Rinse in 1, 2 and 3
Empty 1
Empty 2 in 1 and remove the excess
Empty 3 in 2
Fill 3 by freshwater
Wash the second batch of clothes
Empty 1 and 2, keep 3 for tomorrow.
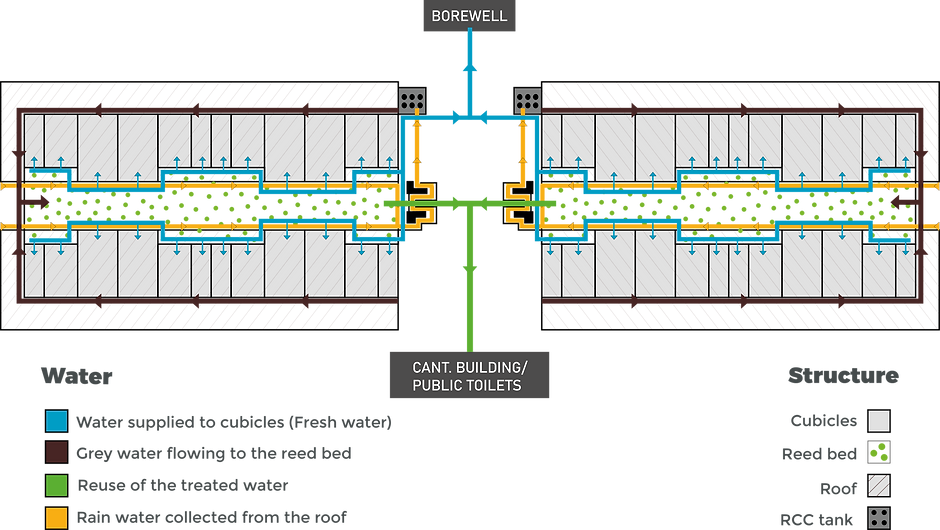
IDEAL WATER SYSTEM
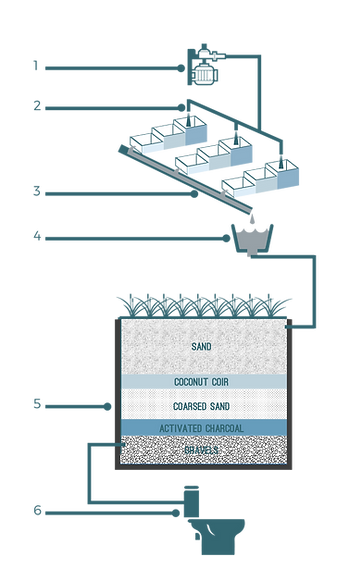
Municipal corporation/ government-provided water/ bore well. (Main source of water)
Connecters attached to the main pipe making multiple supply knobs which then provide water in each cubicle.
Direct drain line carries greywater to the main terminal.
The main terminal collects all greywater which then flows towards the reed bed. (Primary purification)
Goes through sand purification
(secondary purification)Processed water supplied directly to nearby public toilets and government office toilets as flushing water.
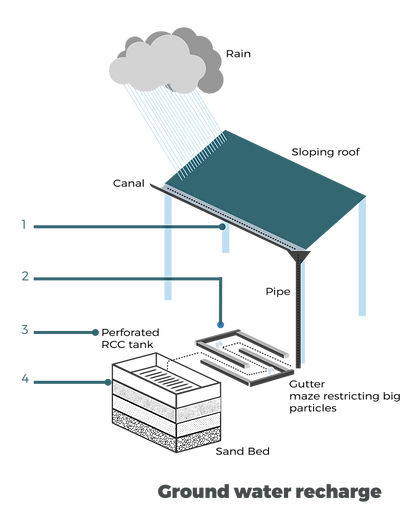
WATER HARVESTING SYSTEM
Water collected from the roof during the monsoon through a channel.
Passes through the maze eliminating big chunks of waste and dry leaves.
Enters the perforated RCC tank.
Passes through the sand bed getting naturally purified.
Recharges the groundwater level which will then be used through the borewell.
IDEAL SYSTEM LAYOUT
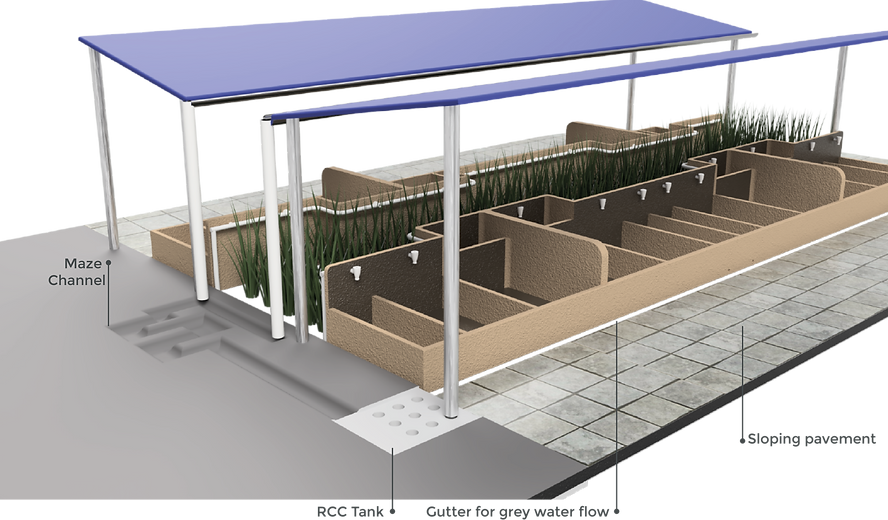
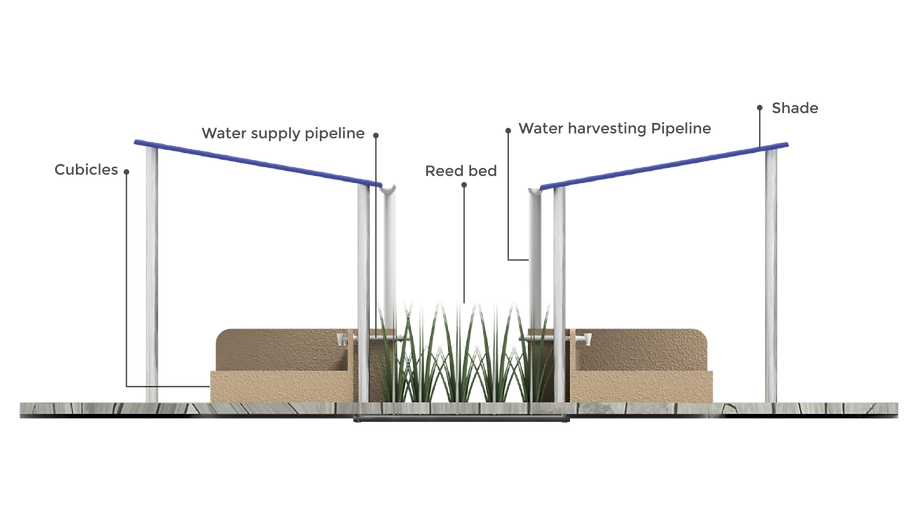


REDUCE
The consumption of water
through modifying the
structure
REUSE
Of greywater by filtration
through reed bed and sand
bed technique for flushing
purposes
RETAIN
Groundwater level by
rainwater harvest
technique and using the
same through borewell
